The brainstorming technique was created by Alex Osborn in 1938. The term refers to the “disconnected thought” or “creative thought”. This tool asks people to leave their mind free to explore new ways, to invent new associations, to abandon old mental patterns. It is based on a group crossed discussion managed by a moderator. The brainstorming discussion provides a list of ideas, which should be used as a hint to solve a specific problem and which could be evaluated and elaborated subsequently.
This technique is based on the consideration that ideas refer to other ones, if they are expressed by different people. This process is metaphorically called cross-fertilization.
The process of brainstorming is very simple: when focusing
on a specific problem this technique allows the group to create as many
solutions as possible, as far as possible, without a pre-established
order (see fig.1). The technique provides a great number of ideas and
the linkages between them stimulate the generation of new proposals,
in an auto-feeding process.
The most important thing which must be taken into consideration during
the discussion is that each idea must be respected and must not be judged
a priori.
The entire process is synthetizable in four main assumptions:
1. Deferred critical judgement
An idea should not be judged or evaluated at the same time in which
it is generated. If the idea is judged, the one who produced it will
try to protect it strongly instead of thinking about other possibly
better ideas. The deferment of the assessment phase represents the most
important feature of the brainstorming.
2. Unconventionality is welcome
Everyone should be stimulated to produce as much unconventional ideas as possible, without being worried to appear ridiculous. In this way everyone’s imagination can act freely.
3. Multiplication of ideas
Quantity rather than quality of ideas must be encouraged. They will be selected later.
4. Encourage the good ideas of other people
When several ideas are generated, everyone is encouraged to take into consideration and to modify other people’s ideas. This produces new ideas, better than the initial one.
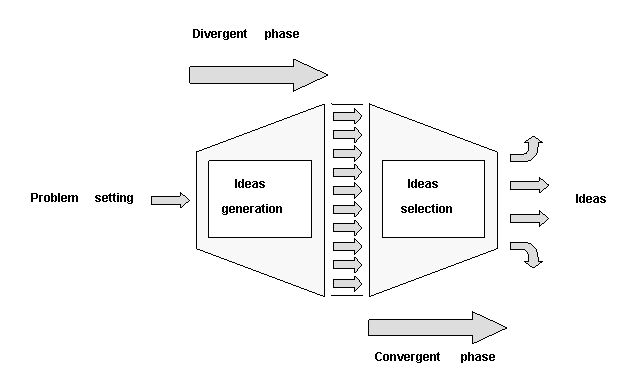
Fig.1. The generation of ideas in the brainstorming process.
The only strictly formal characteristic related with this technique is a written report of all the ideas generated. One or more people should write down each of these ideas, count them later on, without associating the name of the proponent. The list will be used as hints to find a solution for the considered problem.
The duration of a brainstorming session
An empirical rule suggests that the duration of a single brainstorming session should be approximately 30 minutes. If 30 minutes aren’t enough, it means that the problem have to be defined more clearly. If the group has only a short time for the session, then the ideas will probably be superficial.
The best achievable result using brainstorming technique is that, in each session, the group could generate much more good ideas (in a short time) than a traditional discussion. This technique improves creativity and initiative of the individuals.
Research studies demonstrate that this technique could be used both in individual and collective effort. An interesting and fruitful approach is to generate the core idea by yourself and, subsequently, to leave the development phase to the others. This kind of approach usually produces more ideas than the starting author could have done by himself.
Individual brainstorming
It generates a wider spectrum of ideas than the group’s session, but with less efficiency, because often individuals try to give thought to problems that they won’t be able to solve. On the other hand, individual could explore ideas in a better way, without being worried about wasting time or being criticized by someone else and, of course, without being dominated by the other members of the group.
Group brainstorming
It develops ideas more in depth than individual brainstorming.
In fact, individual’s problems in developing ideas could be overcome
by creativity and experience of somebody else.
Group brainstorming produces a smaller number of ideas (because time
is used to develop ideas more in depth rather than to generate them)
and moderate individuals could be repressed by the more noisy ones.
In fact, in every group there are two different kind of people: on one
hand there are intuitive/flexible people, on the other hand there are
strict/logic people. The first category refers to creative thinkers,
which are more fruitful in the initial phase. The second one refers
to critical thinkers, which are useful in discussing about the feasibility
of the generated ideas.
Combining individual and group brainstorming
Individual and group brainstorming could be combined
together. For example, someone defines the problem individually and
leaves the group free to find several superficial solution, if possible.
Then, these solutions could be improved at individual level by specialists
of each topic.
In any case, again as before, it is important to separate the idea’s
generation phase from the assessment phase.
Operative rules for the brainstorming session
This section presents a couple of rules useful for a better direction of a brainstorming session. These rules are:
- Someone must be asked to manage the session, to clearly define
the problem and the objectives to achieve. It is important to leave
the discussion free, without any kind of limitation.
- This facilitator has to encourage an enthusiastic behaviour in
the group, without criticism, and has to spur each participant to
express his/her point of view. It is better to define the duration
of the session from the beginning, while no topic has to be followed
for much time. It is also better to focus the discussion on practical
solutions of the problem.
- The people attending brainstorming sessions should come from different
disciplines, with a wide spectrum of experience, so as to obtain more
creative ideas from the session.
- People should be stimulated to do brainstorming in the most informal
and amusing way, giving all possible ideas, from practical ones to
those that are apparently unfeasible, generating a creative environment.
All ideas will be accepted and registered.
- Ideas must not be criticized or judged during the brainstorming
session. In fact criticism could inhibit individuals to explain his/her
own ideas. This behaviour kills creativity and yields ineffective
sessions. It is easier to unwrap bad ideas at the end of the session,
than generating good ones. At this point the question could be: “don’t
you think this is a waste of time?”. The answer obviously is
no, because these unfeasible ideas could stimulate the others to produce
new original and innovative ideas.
- It is advisable to encourage participants to work on other people’s ideas, in order to improve them.
Limitations of a brainstorming session
Besides positive aspects there are also some limitations of the brainstorming technique that must be taken into consideration. As observed by Osborn (1992), sometimes brainstorming sessions don’t produce results as expected, fundamentally for two main reasons:
- faulty operation: lack of adhesion with procedures based on experience
- overrated expectation: sometimes people forget that miracles do not happen that often.
In synthesis, the result of the brainstorming techniques are the following:
- some sessions could produce effectively final answers, but only
if the problem is easy…
- some sessions could produce hints for further projects
- some sessions could provide check-lists to promote new creative
thoughts
- some sessions could provide an approach to the following problem-solving phase. This is true especially when facing complex problems as technological ones.
- Osborn A.F., The art of creativity, Milan, Franco Angeli,
1992, orig. ed. 1953.
- Bertone V., Business creativity. Methods, techniques; case studies
to enhance the creative potential of managers and entrepreneurs.,
Milan, Franco Angeli, 1993.
Original title: Bertone V.,Creatività aziendale. Metodi, tecniche; casi per valorizzare il potenziale creativo di manager, imprenditori., Milano, Franco Angeli, 1993.
- Cocco G.C., Creativity research and innovation. Individuals
and enterprises opposite the challenges of post-industrial society,
Milan, Franco Angeli, 1987.
Original title: Cocco G.C., Creatività ricerca e innovazione. Individui e imprese di fronte alle sfide della società post-industriale, Milano, Franco Angeli, 1987.